First Express Server
要建立第一個能運作的API非常簡單
// index.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello World')
})
app.listen(3000)
由於Express.js非常早就存在,所以用require比較穩定
Express Router
在有較多API Endpoints時比較好管理
// route.js
const express = require('express')
const router = express.Router()
router.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello, I am router.')
})
module.exports = router
// exports.router = router
// index.js, add two lines
const route = require('route')
app.use('/api', route);
// app.use('/api', route.router)
Logger - Morgan/ Winston
能夠顯示request log的套件有非常多,Morgan是Express.js底下的套件
安裝的方式是npm i morgan,使用起來也很方便
// index.js
var morgan = require('morgan')
// choose a style
app.use(morgan('combined'))
app.use(morgan('tiny'))
實際成果
// combined
::ffff:127.0.0.1 - - [08/Jun/2022:14:00:29 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 11 "-" "Apache-HttpClient/4.5.13 (Java/11.0.13)"
// tiny
GET / 200 11 - 1.675 ms
Middleware
前面用到的自訂router以及morgan都算是middleware,request會先在middleware處理完
之後才會到我們定義的endpoint裡接續處理
如果想要知道request內傳進來的內容,可以透過body-parser這個套件
在Express 4.16後就已經內建body-parser,不用特別去裝
// index.js
app.use(express.json());
// route.js
router.post('/test', express.json(), (req, res, next) => {
res.send(JSON.stringify(req.body));
});
這樣就能將request body內的資料傳給endpoint做處理
Cutom Middleware
這種設定方式會讓所有request在進到各自Endpoint前都會執行myLogger
// index.js
var myLogger = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('LOGGED');
next();
};
app.use(myLogger);
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello World!');
});
next()是為了能正確地把request往下傳遞給對的route
What's CORS?
通常會知道CORS都是在遇到一個很經典的錯誤後
request has been blocked by CORS policy: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource.
這個狀況會發生在你使用前端去fetch不同來源的後端API
而且這個狀況是無法單純靠前端去修正的
來源的限制包含了scheme + host + port,只要任一部分不同都會觸發CORS
解決方式很簡單就是在server端設定Access-Control-Allow-Origin 的 header
通常不會直接門戶大開,而是會去限制有哪些人可以取得我這裡的資料
CORS Package
由於是很早期的套件,就叫cors而已 npm i cors
const cors = require('cors');
// import cors from 'cors'
// enable CORS - Cross Origin Resource Sharing
app.use(cors());
效果和在response header中手動加一樣
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', '*');
});
GET - Query
Query指的是網址最後帶問號的部分,如果有多個值會以&區隔開
GET /something?name=wade&gender=male
Express.js要取得這兩個變數也很簡單
// index.js
app.get('/something', (req, res) => {
// 印出整個query object,裡面包含了有哪些key
console.log(req.query)
// 可以分別取到對應的值,兩種寫法都會work
console.log(req.query.user, req.query['gender'])
})
Query在使用上會比較彈性,可以直接根據需求在網址上新增很多
Server會視自身需求決定要取拿些下來用
GET - Parameter
Parameter會是網址的一部分,所以一開始必須就規劃好
/users/20119338
上面的網址會把最後的區塊給塞入user的id,server只要把最後一塊切下來就能拿到
// index.js
app.get('/sample/:id', function(req, res) {
// req.param('id') is deprecated
var id = req.params.id
})
多數框架都有寫好方便的取法與設計規則,不用自己手動去split URL
有需要的話query和parameter是可以混用的
Controller
Route的部分主要負責將request根據endpoint給導向正確的controller
// index.js
const userController = require('./user.controller')
app.get('/users/:id', userController);
Controller則負責一些簡易邏輯的處理,包含還要將資料傳給那些model
// user.controller.js
const userModel = require('./user.model')
const getInfo = function(req, res) {
var id = req.params.id
console.log(userModel.getName(id))
res.send('done')
}
exports.getInfo = getInfo
Model
Model負責的部分是根據contoller給的資料決定要如何和DB進行互動
// user.model.js
// 這裡應該會是和資料庫互動的部分, ex: SQL
const getName = (id) => {
return 'John'
}
exports.getName = getName
那到目前為止基礎的MVC架構就算完成了(目前還沒有實際的View)
如果我們呼叫http://localhost:3000/users/1234,就能看到Node.js log出John
Dockerfile
把我們的API變成一個docker image,準備如下的Dockerfile在backend資料夾中
FROM node:16-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY ./* /app/
RUN npm i
EXPOSE 3000
CMD npm start
建議在準備一個.dockerignore檔,可以避免把不必要的檔案塞進image內
cd到backend資料夾後,就可以使用docker build -t first_api .來build image
最後使用docker run --rm -itd -p 3000:3000 first_api就能獲得我們的docker container
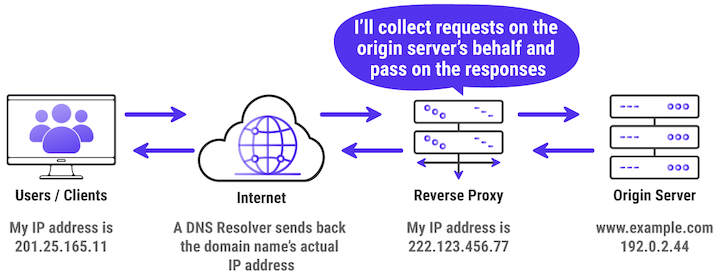
Reverse Proxy
Reverse Proxy可以協助外部使用者將request送到正確的伺服器去
假設我們今天有超過1台的Origin Server,只有一台是平時會啟用的
剩下是當流量增加或是主要的那台壞掉才會上線,由於這些主機的IP都不同
導致我們無法使用單一domain來對應,這時候Reverse Proxy就配上用場了
我們可以藉由Revere Proxy將request自動mapping到空閒的server
Nginx as Reverse Proxy 1/2
透過修改conf檔來把nginx web server變成reverse proxy
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_pass http://api:3000;
}
}
nginx內有許多位置可以放conf檔,像是可以直接修改原始的/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
或是去取代/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf把範例檔給蓋過去
如果是在Ubuntu裝甚至還會有sites-available等資料夾可以設定
Nginx as Reverse Proxy 2/2
把conf檔給複製到客製的image內
FROM nginx:1.21-alpine
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
先build我們自己的reverse proxy docker build -t revers_proxy .
使用docker run -d -p 80:80 --link api:api revers_proxy就可以啟動
記得要啟動前面的API container
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name api first_api
這時候透過localhost或是localhost:3000就能取得一樣的效果了
Docker Compose
一次用docker compose up啟動reverse proxy加上前面的API Container
首先要來撰寫docker-compose.yml檔,它裡面指定了我們要使用那些image來啟動container
version: "3"
services:
api:
build: .
image: first_api
ports:
- "3000:3000"
reverse-proxy:
build: nginx/.
image: reverse_proxy
ports:
- "80:80"
Fastify
Part 02
What's Fastify?
Fastify主要是做為後端框架使用,frontend可以搭配主流的三大前端框架
作為後端框架擁有非常高的throughput,能夠在單一時間處理較多request
且完美支援HA機制以及現在必備的TypeScript
安裝方式是npm i fastify --save

First Fastify Server
Fastify相對而言是一個比較新的框架(看Doc頁面也能感受出)
import Fastify from 'fastify'
const fastify = Fastify({
logger: true
})
// Declare a route
fastify.get('/', function (request, reply) {
reply.send({ hello: 'world' })
})
// Run the server!
fastify.listen(3000, function (err, address) {
if (err) {
fastify.log.error(err)
process.exit(1)
}
})
Beautify Logs 1/2
預設顯示log的方式其實相當雜亂
{"level":30,"time":1617089076094,"pid":29400,"hostname":"HOSTNAME","msg":"Server listening at http://127.0.0.1:3000"}
{"level":30,"time":1617089142419,"pid":29400,"hostname":"HOSTNAME","reqId":"req-1","req":{"method":"GET","url":"/","hostname":"127.0.0.1:3000","remoteAddress":"127.0.0.1","remotePort":52883},"msg":"incoming request"}
{"level":30,"time":1617089142436,"pid":29400,"hostname":"HOSTNAME","reqId":"req-1","res":{"statusCode":200},"responseTime":15.840407997369766,"msg":"request completed"}
可以透過設定去美化以及決定要顯示那些內容
// only show info
const fastify = Fastify({
logger: {
level: 'info',
transport: {
target: 'pino-pretty'
}
}
})
這裡用到的套件pino-pretty要額外裝套件 npm install --save pino-pretty
Beautify Logs 2/2
以往還可以用prettyPrint去美化log,但現在已被棄用
// const fastify = Fastify({
// logger: {prettyPrint: true}
// })
pino-pretty的實際成效會是
[1617089180087] INFO (29392 on HOSTNAME): Server listening at http://127.0.0.1:3000
[1617089181725] INFO (29392 on HOSTNAME): incoming request
req: {
"method": "GET",
"url": "/",
"hostname": "127.0.0.1:3000",
...
Async-Await Style
除了express式的return funtion外,也支援在endpoint直接使用async加上await
const fastify = require('fastify')({
logger: true
})
fastify.get('/', async (request, reply) => {
return { hello: 'world' }
})
const start = async () => {
try {
await fastify.listen({ port: 3000, host: '0.0.0.0' })
} catch (err) {
fastify.log.error(err)
process.exit(1)
}
}
start()
Plugin 1/2
這裡的plugin相當於前面express.js提到的route
首先要把原本的server.js給改寫成
import Fastify from 'fastify'
import firstRoute from './first-route'
const fastify = Fastify({
logger: true
})
fastify.register(firstRoute)
fastify.listen({ port: 3000, host: '0.0.0.0' }, function (err, address) {
// ...
})
透過register把plugin給fastify使用,和express的app.use()同理
Plugin 2/2
再來要去寫route裡面的內容,其實就是把原本endpoint內的function給搬進來
// first-route.js
async function routes (fastify, options) {
fastify.get('/', async (request, reply) => {
return { hello: 'world' }
})
}
export default routes
一樣透過npm start就可以去測試改寫成plugin版的API
export function前面的async是必須的,這樣fastify在註冊時才會一直等request
如果沒有async的話,fastify server在時間到前都沒等到request就會自動報錯結束
Fatify-Plugin
基本上就是Express.js中的middleware概念
可以搭配自家的套件進行使用會更方便,像是@fastify/mongodb
下面會舉更多例子
Fastify Cookie
Cookie基本上都是由後端告訴瀏覽器要存的,所以需要先安裝套件npm i @fastify/cookie
fastify.register(require('@fastify/cookie'), {
secret: "my-secret", // for cookies signature
hook: 'onRequest', // set to false to disable cookie autoparsing
parseOptions: {} // options for parsing cookies
})
fastify.get('/', (req, reply) => {
const aCookieValue = req.cookies.cookieName
reply.setCookie('foo', 'foo', {
domain: 'example.com',
path: '/'
}).send({ hello: 'world' })
})
Fastify Session
可以在server暫時保存較長期的資料,分常適合在頁面跳轉後繼續保留資料
要在瀏覽器中記錄sessionId所以得搭配cookie套件去做使用
const fastifySession = require('@fastify/session');
const fastifyCookie = require('@fastify/cookie');
const app = fastify();
app.register(fastifyCookie);
app.register(fastifySession, {secret: 'a secret with minimum length of 32 characters'});
app.get('/', (request, reply) => {
reply.send(request.session.authenticated)
})
app.post('/login', (request, reply) => {
const { email, password } = request.body
if (password === 'abcdef') {
request.session.authenticated = true
reply.redirect('/')
}
})
Fastify CORS
當我們前後端的port或是IP不一樣時就會觸發瀏覽器的CORS保護機制
要繞過這個保護機制的限制話,只能在backend端去做設定
設定方式也很簡單只要回傳允許的CORS的header,先安裝套件npm i @fastify/cors
await fastify.register(require("@fastify/cors"), {
origin: "*",
methods: ["POST"]
})
// ...
Format Respone
可以規定respone要回傳的格式,在不符合時就會報錯
const opts = {
schema: {
response: {
200: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
hello: { type: 'string' }
}
}
}
}
}
fastify.get('/', opts, async (request, reply) => {
return { hello: 'world' }
})
GET - Query & Parameter
不是只有GET才能帶query,只是通常是用在GET
fastify.get('/query', async (request, reply) => {
const name = request.query.name
return name
})
fastify.get('/param/:id', async (request, reply) => {
const getId = request.params.id
return getId
})
基本上用法都和在Express.js時差不多
Parse Request Payloads
基本上就是Express.js的bodyParser部分
能夠處理會帶content的http method,像是POST跟PUT
Fastify預設會自動去parse JSON跟text,所以不用額外設定
// server.js
const opts = {}
fastify.post('/info', opts, async (request, reply) => {
const myBody = request.body
reply.code(201)
return {'name': myBody.name, 'gender': myBody.gender}
})
通常新增/修改資料成功會用status code 201
這裡預設還是用200所以要自己修改
Test API with Jest 1/3
前面已經講過了怎麼使用GET和POST,現在可以來寫test case去測試他們
實際上執行TDD的開發上會先寫test case才開始寫邏輯,套件裝法是npm install -D jest
在開始寫test case前必須要把API server的環境準備好,這需要把server包成function
// server.js
const start = () => {
fastify.listen(3000, '0.0.0.0', function (err, address) {
if (err) {
fastify.log.error(err)
process.exit(1)
}
return fastify
})
}
export {start}
Test API with Jest 2/3
如果要把多個case包成一組會在最外面用describe
test case的開頭可以使用test或是it,實際執行test可以用npx jest
// server.test.js
import { start } from './server'
describe('first test suite', ()=> {
beforeAll ( () => {
server = start()
})
it('test get', async () => {
const response = await server.inject({ method: 'GET', url: '/' })
expect(response.statusCode).toBe(200)
expect(response.body).toStrictEqual(JSON.stringify({ hello: 'world' }))
})
})
Test API with Jest 3/3
test case的部分由於要等實際server回傳所以得用async await
啟動和關閉server的部分也建議用async await
// server.test.js
describe('first test suite', ()=> {
beforeAll ( async () => {
server = start()
await server.ready()
})
afterAll ( async () => {
await server.close()
})
// ...
})
Run CI on Azrure DevOps
CI指的是continuous integration,簡單來說就是在code寫完後要自動做一些事
比較常見的像是準備docker image有利於未來deploy以及自動跑test case確保程式沒有錯誤
所以今天的目標是要學會用Azure Devops達成以下:
- Build Image
- Run Jest test
CI Pipeline - Build Image
azure-pipelines.yml
trigger:
- express_js
resources:
- repo: self
variables:
tag: '$(Build.BuildId)'
stages:
- stage: Build
displayName: Build image
jobs:
- job: Build
displayName: Build
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- task: Docker@2
displayName: Build an image
inputs:
command: build
dockerfile: '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/backend/Dockerfile'
tags: |
$(tag)
CI Pipeline - Run Test
在前面的pipeline基礎上修改steps,裡面再多加一個task
steps:
- task: NodeTool@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '16.x'
displayName: 'Install Node.js'
- script: |
npm install
npm run test
displayName: 'npm install and run test'
workingDirectory: 'backend'
CI Pipeline - Jest Code Coverage
在package.json內要多一個coverage的script
"scripts": {
"coverage": "jest --coverage --coverageReporters=cobertura"
},
只要從task下的script開始改就好
- script: |
npm install
npm run coverage
displayName: 'npm install and output coverage'
- task: PublishCodeCoverageResults@1
inputs:
codeCoverageTool: Cobertura
summaryFileLocation: $(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/backend/coverage/cobertura-coverage.xml
CI Pipeline - Test Tab 1/2
如果要在Azure DevOps上顯示test分頁,就會需要junit的xml檔
jest有對應的套件可以產出juint的xml檔,但要額外安裝npm install jest-junit --save-dev
"jest-junit": {
"suiteNameTemplate": "{filepath}",
"outputDirectory": ".",
"outputName": "junit.xml"
},
"scripts": {
"test:ci": "npm run test -- --watchAll=false --reporters=default --reporters=jest-junit",
},
要在package.json中設定輸出的路徑以及如何執行
CI Pipeline - Test Tab 2/2
最後還要補上底下的task
- task: Npm@1
displayName: npm run test
inputs:
command: 'custom'
workingDir: 'backend'
customCommand: 'run test:ci'
- task: PublishTestResults@2
displayName: 'supply npm test results to pipelines'
condition: succeededOrFailed() # because otherwise we won't know what tests failed
inputs:
testResultsFiles: 'backend/junit.xml'
More Test Cases - GET
接著繼續測試其他前面提過的不同類型endpoint
it('test get query', async () => {
const response = await server.inject({ method: 'GET', url: '/query?name=John' })
expect(response.statusCode).toBe(200)
expect(response.body).toStrictEqual('John')
})
it('test get parameter', async () => {
const response = await server.inject({ method: 'GET', url: '/param/1234' })
expect(response.statusCode).toBe(200)
expect(response.body).toStrictEqual("1234")
})
More Test Cases - POST
post的部分在inject時要放入資料
it('test post', async () => {
const response = await server.inject({ method: 'POST', url: '/info', payload: {
name: 'John',
gender: 'male'
} })
expect(response.statusCode).toBe(201)
const resBody = JSON.parse(response.body)
expect(resBody.name).toStrictEqual('John')
expect(resBody.gender).toStrictEqual('male')
})
注意POST成功的code是201而非200
MongoDB
前面講為了許多API Server的基本使用方式,現在終於可以開始介紹DB
今天我們會用比較好上手的MongoDB,這樣就算對SQL語法不熟悉也沒關係
MongoDB是一種NoSQL Database,代表的是Not Only SQL
比較常見的好處有以下:
- 是一款高效能且開源的DB (有另外針對企業優化的付費版)
- 資料欄位比較彈性,以JSON儲存,在Monogo內稱為Document
- 適合大量資料,因為有較好的水平擴展性,可以透過資料分片(Sharding)
- Query data的方式比SQL語法容易上手,且內建多種aggregation的方法
- MongoDB本身就有提供hosting的服務(和雲端三大廠聯手),擁有免費方案
GUI Tools
- VScode插件
- Datagrip
- MongoDB Compass
- Studio 3T/ Robo 3T
Mongoose
我們今天不會直接使用mongo shell來和db互動,而是會用一個包好的套件叫mongoose
mongoose是專為js設計的,所以有考慮到asynchronous
安裝方式一樣很簡單就是npm i mongoose
mongoDB本體的安裝則會使用docker
docker run --name some-mongo -d -p 27017:27017 \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=mongoadmin \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=secret \
mongo:5.0.9
port要記得往本機mapping,這樣等等才能使用
如果要在啟動時順便建立admin帳號就要透過環境變數去設定使用者
Simaple Use Case 1/2
使用時要先和DB進行連線
// db.js
import mongoose from 'mongoose'
const host = process.env.MONGO_HOST || 'localhost'
const port = process.env.MONGO_PORT || 27017
const database = process.env.MONGO_DATABASE || 'fastify'
const establishConnection = () => {
// const connectionString = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/myProject'
if (mongoose.connection.readyState === 0 && !process.env.JEST_WORKER_ID) {
mongoose.connect(`mongodb://${host}:${port}/${database}`,
(err) => {
if (!err) console.log('MongoDB connection successful.')
else console.log('Error in DB connection : ' + JSON.stringify(err, undefined, 2))
}
)
}
}
export {establishConnection}
Simaple Use Case 2/2
在主程式中去呼叫mongodb連線的function
// server.js
import {establishConnection} from './db'
server.listen(()=> {
// ...
establishConnection()
})
再來要先定義一下collection中的大致schema
// model.js
import { model, Schema } from 'mongoose'
const personSchema = new Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true }
})
const person = model('Person', personSchema)
CRUD
接著要定義model如何去和DB互動
// model.js (接續前面)
// C
person.create({ name: 'John', height: '170cm'}, function(err, res) {
// check success or not
})
// R (Query)
person.find({ name: 'John'})
// U
person.updateOne({ name: 'John' }, { name: 'Bear' }, function(err, res) {
// Updated at most one doc, `res.nModified` contains the number of docs that MongoDB updated
});
// D
person.deleteOne({ name: 'John' }, function (err) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
// deleted at most one tank document
});
Test Case with MongoDB
當然可以直接對現有的DB進行CRUD的測試,但會搗亂現有的資料庫
因此比較好的做法有像是in-memory的db或是test container
那今天先示範的是前者,我們這裡會使用mongo-memory-server這個套件
一樣只要透過npm i mongodb-memory-server去安裝就好
他會實際去幫你裝mongodb,之後做test時會去啟動他,且資料只會保存在測試期間
import { MongoMemoryServer } from 'mongodb-memory-server';
// This will create an new instance of "MongoMemoryServer" and automatically start it
const mongod = await MongoMemoryServer.create();
const uri = mongod.getUri();
// The Server can be stopped again with
await mongod.stop();
Jest with mongodb-memory-server 1/4
首先要把啟動mongodb-memory-server的部分給先包成function, 方便等等Jest call
// in-memory-db.js
import mongoose from 'mongoose'
import { MongoMemoryServer } from 'mongodb-memory-server'
const mongod = new MongoMemoryServer()
// Connect to mock memory db
export const connect = async () => {
await mongod.start()
const uri = mongod.getUri()
await mongoose.connect(uri)
}
// Close db connection
export const closeDatabase = async () => {
await mongoose.connection.dropDatabase()
await mongoose.connection.close()
await mongod.stop()
}
Jest with mongodb-memory-server 2/4
如果要把現在的db清空的話還可以加上
// in-memory-db.js
// Delete all db collections
export const clearDatabase = async () => {
const collections = mongoose.connection.collections
for (const key in collections) {
const collection = collections[key]
await collection.deleteMany({})
}
}
Jest with mongodb-memory-server 3/4
接著把這些function給對應到test suite中的各個部分
// server.test.js
import * as dbHandler from './in-memory-db'
describe('xxx', () => {
// ...
beforeAll(async () => {
await dbHandler.connect()
})
afterEach(async () => {
await dbHandler.clearDatabase()
})
afterAll(async () => {
await dbHandler.closeDatabase()
})
// ...
})
Jest with mongodb-memory-server 4/4
由於DB一開始是空的如果要測試RUD的話,一定得先透過POST去創建一些資料
可以選擇在beforeAll()時去固定創建一些假資料,或是在每個test case都先inject資料
it('xxx', async () => {
// POST first
const response = await server.inject({ method: 'POST', url: '/info', payload: {
name: 'John', gender: 'male'
}
})
// Then GET
const response2 = await server.inject({ method: 'GET', url: '/info' })
expect(response2.statusCode).toBe(200)
})
這裡假定POST的/info endpoint會把資料給存進mongodb
然後GET的/info endpoint會把資料存mongodb給讀出來
Practice - Put? Delete?
現在可以來自行練習寫PUT跟DELETE的Endpoint
PUT
寫法和POST基本上一致
fastify.put('/db', (request, reply) => {
person.updateOne({ name: request.body.name, height: request.body.height}, { name: 'ha', height: 'ha' }, (err, result) => {
return reply.status(201).send('data updated')
})
})
Test Case的話
it('update', async () => {
const response = await server.inject({ method: 'POST', url: '/api/db',
payload: { name: 'John', height: 170 }
})
const response2 = await server.inject({ method: 'PUT', url: '/api/db',
payload: { name: 'John', height: 170 }
})
expect(response2.statusCode).toBe(200)
})
DELETE
是可以有body的,但不是所有框架都支援
這裡會用parameter來傳遞要刪除的資訊
fastify.delete('/db', (request, reply) => {
person.deleteOne({ name: request.params.name }, function (err) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
return reply.status(204).send('Content deleted')
})
})
Test case寫法也雷同
it('update', async () => {
const response2 = await server.inject({ method: 'DELETE', url: '/api/db',
payload: { name: 'John' }
})
expect(response2.statusCode).toBe(200)
})
Service
他算在MVC架構中的controller底下,可以避免controller本身過於複雜
EX: 假設有個Member的controller要負責CRUD,且每個的商業邏輯都很複雜
就可以多一層service來處理商業邏輯部分,controller只要指定用哪個service的function
所以在實作上通常會是controller -> service -> model
如果處理的邏輯並沒有負責到要和controller分離,沒有這層也沒有關係
這次只是簡單的入門範例,所以只要有概念就好
Repository Pattern
Service本身應該著重於讀取資料這件事,盡量不去處理和邏輯相關的(尤其DB)部分
這時我們就會將邏輯相關部分給抽離至Repository
這樣做的好處也相對明顯,當不同service要調用相同資料時可以共用Repository
所以現在的架構會變成controller -> Service -> Repository -> Model
他能減少未來換不同種資料庫所要修改的程式範圍,接著就來實作
CRUD with Repository Pattern 1/2
我們可以把之前全部寫在db-route.js中的mongoose語法都給抽離到repo去
// person.repo.js
import person from "./db.model"
class PersonRepo {
static of() {
return new PersonRepo()
}
async getPerson() {
return person.find()
}
async addPerson(requestBody) {
return person.create({name: requestBody.name, height: requestBody.height})
}
}
export { PersonRepo }
CRUD with Repository Pattern 2/2
由於改成promise的寫法,不能像之前callback一樣return result + error
這裡我們就要用try, catch去避免任何的錯誤發生
// db-route.js
import { PersonRepo } from "./person.repo"
fastify.post('/db', async (request, reply) => {
const person = PersonRepo.of()
try {
const requestBody = request.body
const result = await person.addPerson(requestBody)
return reply.status(201).send( {result} )
} catch (err) {
return reply.status(500).send( { msg: err })
}
})
Refactor Practice - Put? Delete?
現在可以來練習修改PUT跟DELETE的Repo Pattern
Summary in MVC + Service & Repository
這套邏輯主要被用在Spring框架與ASP.NET上,可以大幅降低程式複雜度並提高可維護性
我們這裡總結一下各部分專司的職責:
View: 專注於資料的呈現頁面Controller: 負責 API 的接口Service: 處理背後的商業邏輯Repository: 統一定義撈取資料的方式Model: 將內部資料需求與資料庫欄位進行對照
總結來說,多了repo的好處在將來要換DB時,只要去改model中的實作方法即可
OpenAPI/ SwaggerAPI Spec
Part 03
OpenAPI
可以用yaml或是JSON來撰寫API的規格書,不僅能當成document分享也利用設計
VScode Extensions
- Swagger Viewer
- OpenAPI (Swagger) Editor
HTTP Methods and Status Code
- Methods
- GET: 200
- POST, PUT, DELETE: 204
- Status Code
- 200 OK
- 204 No Content
- 400 Auth Failed
- 404 Not Found
Syntax
基本規格的定義
openapi: 3.0.3
info:
title: SwaggerAPI demo - OpenAPI 3.0
description: |-
Some texts or markdown here
termsOfService: http://swagger.io/terms/
contact:
email: apiteam@swagger.io
license:
name: Apache 2.0
url: http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
version: 1.0.11
servers:
- url: https://petstore3.swagger.io/api/v3
Add Endpoints 1/2
定義一個endpoint要如何使用以及會回傳甚麼
tags:
- name: pet
description: Everything about your Pets
paths:
/pet:
put:
tags:
- pet
summary: Update an existing pet
description: Update an existing pet by Id
requestBody:
description: Update an existent pet in the store
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Pet'
required: true
Add Endpoints 2/2
接續前頁的response
responses:
'200':
description: Successful operation
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Pet'
requestBody和respone的content可以是text/plain, application/json等
Schema - Object
定義該類別會需要的資料
components:
schemas:
Order:
type: object
properties:
id:
type: integer
format: int64
example: 10
shipDate:
type: string
format: date-time
complete:
type: boolean
Schema - Enum
列舉所有選項
components:
schemas:
Order:
type: object
properties:
status:
type: string
description: Order Status
example: approved
enum:
- placed
- approved
- delivered
Schema - Array
可以放下多個固定格式的內容
components:
schemas:
Order:
address:
type: array
xml:
name: addresses
wrapped: true
items:
type: object
properties:
name:
type: string